AccentOS. Complete cloud solutions
What is AccentOS?
AccentOS is an OpenStack-based solution with an emphasis on developing functionality that is missing for operators and corporate clients.
OpenStack is OpenSource alternative to VMware, Hyper-V (since 2010, >100 thousand), incl. IBM, RedHat, Cisco Systems, Huawei, Oracle, etc.
Implementation of general architectural solutions, FT platform, HCI, metrocluster, HA for cloud resources.
Implementation of shared AccentOS cloud services includes storage virtualization, VDI, live migration, load balancing, VM resizing, cluster file system.
Automation of the work of AccentOS system administrators - FirstBoot, Backup, scaling, Tap-aaS, Monitoring, remote access, testing, autorecovery, AppLevel).
Security includes authentication, role separation, logging.
AccentOS for private clouds
AccentOS focuses on the development of OpenStack in terms of the private cloud functions that companies lack (qualification, autonomy, information security).
1. Installation - Quick deployment and recovery of the cloud.
2. Hardware infrastructure – Metrocluster, HCI, Storage virtualization, high server availability, public cloud backup.
3. Services - high availability of VMs, live migration of VMs and block devices, cluster OS OCFS2.
4. Ready-made platforms for private cloud projects - VM image management, event scheduler, container management.
5. Desktop virtualization and application delivery.
6. Automation of the work of system administrators (FirstBoot, Backup, Zabbix, Tap-aaS, autorecovery).
AccentOS for operators
Development of OpenStack in terms of functions missing for operators and hybrid cloud (scaling, automation, network services).
1. Rapid deployment of the cloud to the data center, deployment through containers.
2. Operator platform performance – NUMA, CPU pinning, Huge pages, SR-IOV, DPDK for implementing operator network services.
3. Services - NFV (OpenStack Tacker) – OvS, SDN (OvN), SDS (Ceph).
4. Configurations for clients - VDC, VPC, IaaC, PaaS, OSS/BSS.
5. PaaS - Delivery and dynamic provision of platforms and applications to clients (K8-aaS, DaaS, IaaC, DBaaS, BaaS).
6. Hybrid cloud for operators and AccentOS customers.
7. Automation of the work of system administrators (FirstBoot, Backup, Zabbix, Tap-aaS, autorecovery).
AccentOS native characteristics.
-
Minimally modified OpenStack Train/2023.1 Antelope.
-
OS Alt 8 SP 10, Astra Linux 1.7 (1.6), RedHat 8.x, CentOS 8.x, Debian 9/10, Ceph.
-
Supports CPU x86/x64, ARM, Power 9, vGPU NVidia, Intel GPU.
-
Support for Ethernet, iSCSI, iSer, RDMA, FC network interfaces.
-
Support for Linux IPv4, IPv6, SRv6 network protocols.
-
Management of hypervisors Acropolis, Hyper-V, KVM, Xen.
-
Managing LXC, Docker and bare-metal containers.
-
Support for Magnum modules (K8-aaS), ZUN management (PODs).
-
High performance features NUMA, DPDK, SR-IOV, CPU-pinning, HugePages, io_uring, etc.
-
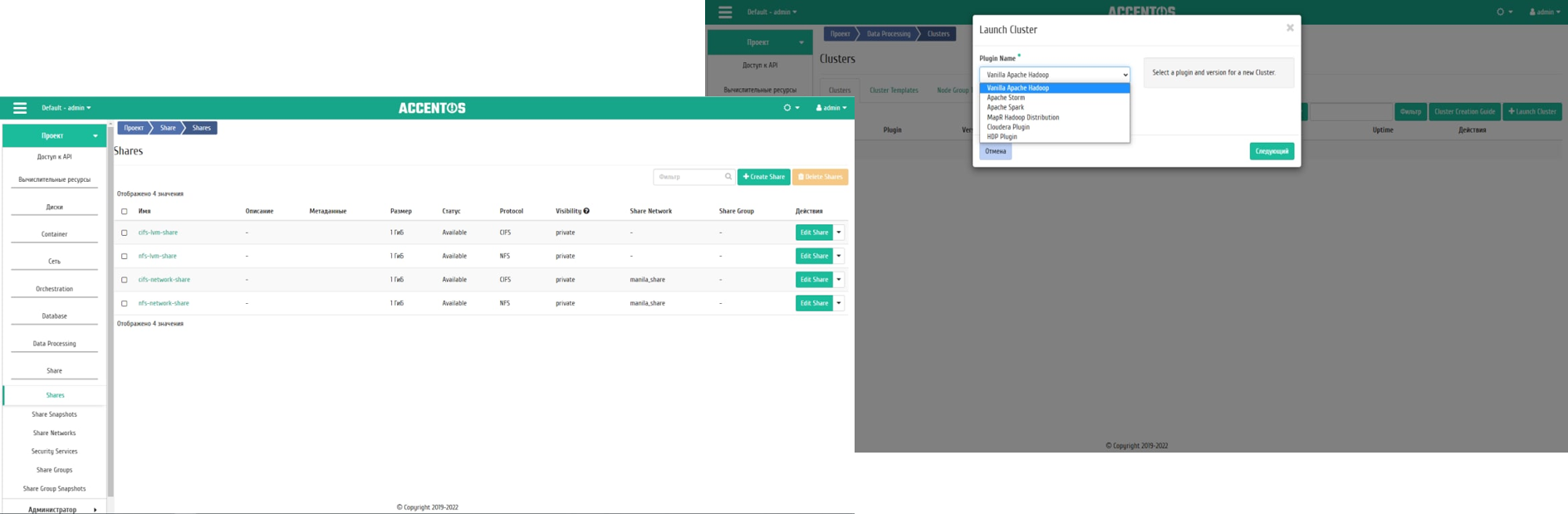
Support for Trove (DB-aaS), Manila (Fileshare-aaS), VPN-aaS, etc. modules.
AccentOS implemented features.
-
High availability of servers and virtual machines.
-
Virtual storage system - connecting proprietary storage systems without drivers.
-
Network segmentation system in data centers.
-
Complete VDI solution and application delivery.
-
Live migration of VMs and block storage devices.
-
Change VM parameters on the fly.
-
Extensions for Horizon, turbo-UI, multilingual interface.
-
Separation of administrator rights (overlay application).
-
Managing “golden images” of virtual machines.
-
Load balancing for hosts and processors.
-
Monitoring and auto-recovery functionality.
-
Cloud backup and recovery.
-
Centralized configuration.
AccentOS 3.0.
New in AccentOS 3.0:
- Support for Linux 6.x with improved virtualization functionality, version adapted for licensed operating systems.
- Support for fully qualified domain names for the instance hostname.
- Improved MariaDB database for storing key configuration data.
- Increasing the OpenStack release cycle to 12 months reduces the frequency of updates.
- Automatic system deployment using podman containers.
- Support for search attributes in Flavor (CPU, RAM, etc.), obtaining a filter for the list of attributes by deployment ID and key.
- Create a cluster instance from a list of templates.
- Update and display quota information when the cluster changes.
- Using an availability zone in several projects, incl. "IN-ADDR.ARPA classless delegation" (RFC 2317), which allows you to assign DNS PTR records to IP addresses in small blocks without creating a DNS zone for each address.
- Magnum support in the admin UI platform.
- Support for global navigation in the upper left corner of the page, progress bar, adding cancellation when using a modal form when uploading a file.
In the field of equipment management:
- CPU power may be limited by the system.
- Full vGPU control function, similar to Nova.
- Support for live migration of virtual machines with GPUs.
- API for GPU attribute lifecycle management.
- PCI devices are monitored and maintained locally on the server.
- Unified management of a variety of devices, such as FPGAs.
- Host naming by FQDNs has become available.
- Disk devices are named by UUID to avoid confusion.
- Added support for expanding attachable volumes for Cinder.
- New server drivers have been added to the Cinder block storage module: HPE XP iSCSI and FC, Fungible NVMe-TCP, NetApp NVMe-TCP storage drivers.
- Added support for Trisync replication for the Pure driver, support for volume group group snapshots for the IBM SVF driver, Unisphere 10 support for the Dell EMC PowerMax driver, and host based migration and retype support for the Hitachi VSP driver.
In the field of security:
- Implemented a role model (sRBAC) for the Neutron network control module.The Glance module applies sRBAC role model policies by default.
- Authentication of external servers using OAuth 2.0 Mutual-TLS has been implemented.
- Implemented SSL Keystone verification via configuration in Skyline UI.
- Logging UI Skyline without a hard path.
- Added support for deploying the validate-config CLI, which will validate service configuration files using oslo-config-validator.
- Trove service deployment now supports internal TLS.
- Nginx.conf.j2 supports both http and https (default is http).
- If you select API microversion 2.95, evacuated virtual machines will remain stopped on the target host until they are manually started.
For operators:
- Added support for the resource allocation API in the Blazar command line client, allowing you to understand which hosts are allocated to each reservation.
- Added random selection option for physical host reservation.
- Implemented a load balancer with various scenarios.
- Implemented placement of tunneled networks and shared resources.
- Enabled host multi-segment support for the ML2/OVS driver.
- Implemented Neutron dynamic routing using ML2/OVN.
- An OVN agent has been created that implements functions not provided by the ovn controller. The metadata service will be migrated first.
- Improved Tacker (MANO) module UI support for NFV services.
- Automatic CNF scaling via performance management threshold interface.
- Updating the network configuration using the current VNF package API.
- AutoHeal and AutoScale are run by external monitoring tools such as Prometheus without NFVO.
PaaS:
- Implemented improved integration of networking functions with Kubernetes.
- The Magnum module has been updated to support Kubernetes v1.24 running on Fedora CoreOS 36 and 37.
- All containerized system services now run in Podman containers.
- Support for some new options when creating a zun container.
- APIs for transferring shared resources between projects are available for the network file system.
- Users can specify metadata when creating their shared networks. The behavior should be similar to Manila shares, and users will be able to update and delete resource data metadata.
- Advanced capabilities for rapid deployment of AI platforms, including Sahara (ML Hadoop, Spark -aaS).
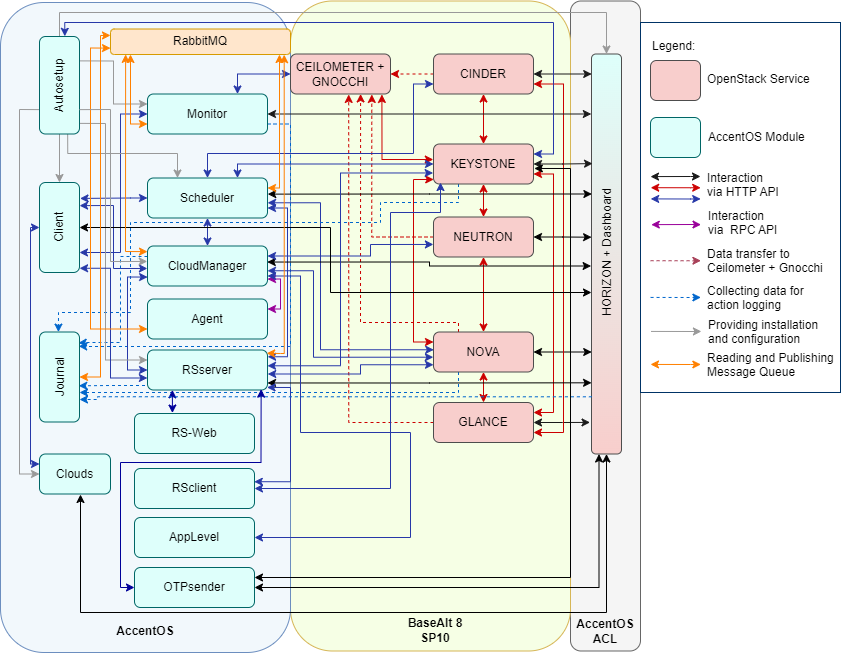
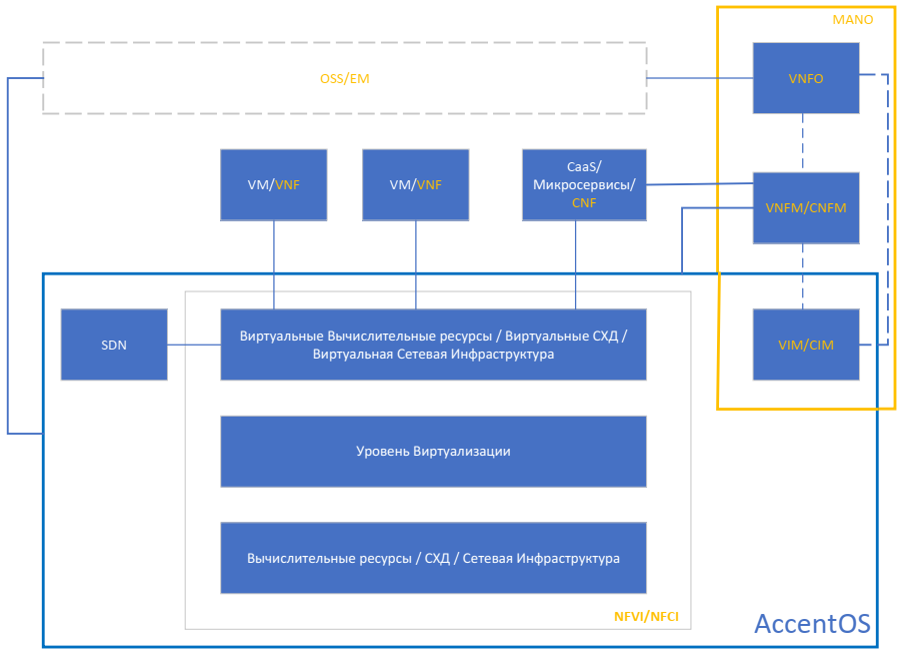
AccentOS architecture
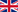
Integration of AccentOS Basalt and AccentOS ACL
AccentOS
for service providers
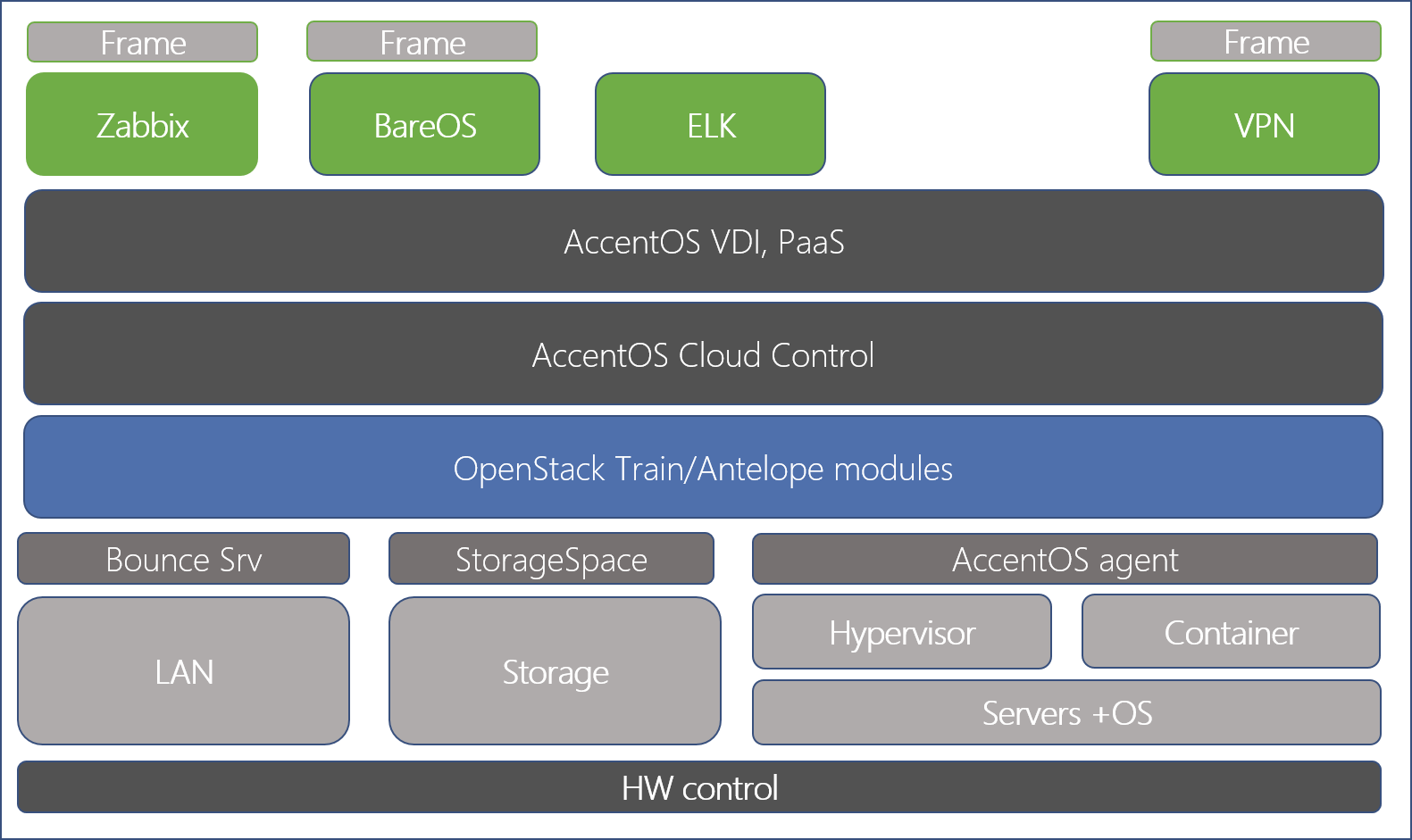
AccentOS Topology and Geodistributed Cloud
AccentOS implements a geo-distributed cloud (metrocluster), which allows to:
- Provide data center redundancy, including SDS storage;
- Implement a cloud FT platform;
- Distribute power in data centers;
- Provide the opportunity to implement FT at the level of client application systems.
Hybrid clouds
AccentOS implements a hybrid cloud, integrating the local resources of the client’s IT infrastructure and the cloud resources of the IaaS provider.
This approach allows to:
- Reduce response time by bringing services closer to external and corporate clients;
- Ensure quick connection of additional resources;
- Increase application fault tolerance;
- Scale project resources;
- Reduce the cost of services.
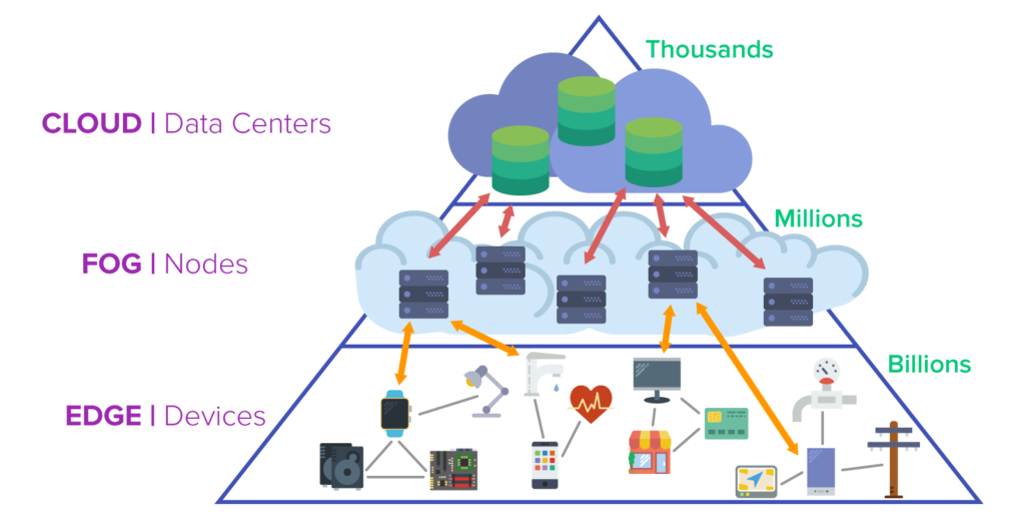
Edge computing and IoT (Edge clouds)
AccentOS supports Edge Clouds, allowing to:
- Reduce response time by bringing services closer to distributed clients;
- Ensure simple and quick connection of additional cloud nodes;
- Ensure application autonomy when communication with the cloud is lost;
- Reduce the cost of services.
High performance cloud operator
AccentOS supports all OpenStack productivity features:
- Real time KVM – setting parameters;
- NUMA is application distribution;
- CPU-pinning of critical applications;
- Huge pages to speed up operations with network buffers (TLB lookups);
- Hardware virtualization technology to speed up the operation of SR-IOV controllers;
- DPDK technology (OvS DPDK) to accelerate the network exchange of VM applications with a virtual switch;
- OVS is hardware offloading with Mellanox 5.
NFV operator services
AccentOS supports OpenStack networking services and running external services:
- OVS + LACP + DVR is distributed management of virtual switches;
- OVN is virtual router management:
-
- Support for network functions at the virtualization environment level: 802.1Q tagging (VLAN).
- Support for network functions at the virtualization environment level: QoS.
- VM traffic mirroring.
- Prohibition of changing the MAC address for the vNIC of a VM.
- Checking the ability to define virtual functions (VFs) in certain physical functions (PFs), including between network cards from different manufacturers (Intel / Mellanox)
- Continuation of correct operation of the SDN data plane (tenant traffic) in the event of failure of the SDN control plane (controller).
- VXLAN support for creating overlays on top of the DC IP network (underlay), SW VTEP.
- Availability of a DHCP/DHCPv6 server for automatic configuration of IPv4/IPv6 in overlay tenants.
- Support for the SLAAC mechanism for automatic IPv6 configuration in overlay tenants.
- LBaaS is a network load balancer.
- vEPC, GiLAN, VoLTE/vIMS are used functions of mobile operators;
- OpenRAN 5G management is through deployment and management of K8s, Docker, VMs.
SDN operator service
AccentOS is compatible with OpenStack Neutron.
OvN supports:
- Services: L2, L3, BGP L3VPN, EVPN, ACL, DHCP, QoS, SFC, IPv6, L2GW;
- OpenFlow protocol and OVS DB-based devices;
- BGP protocol for interoperability with previously released routers.
AccentOS
for corporate clients
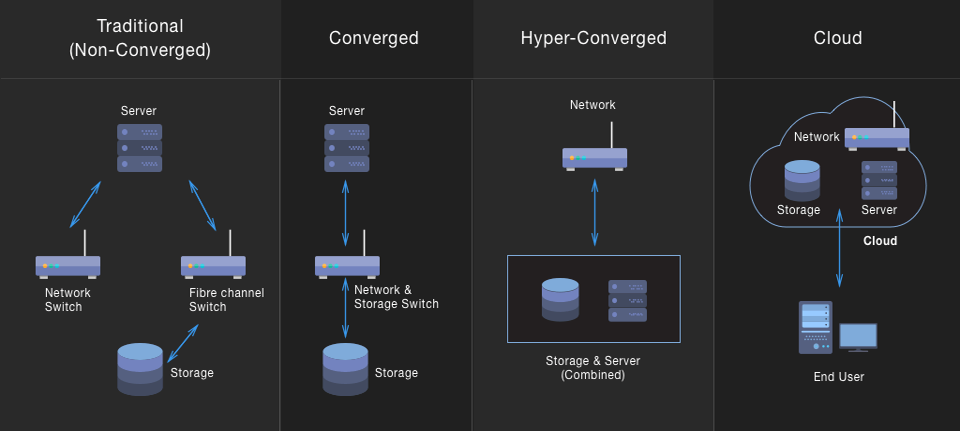
Converged and hyperconverged architecture
AccentOS supports classic architecture with services distributed across nodes and hyperconverged (HCI), when computing, networking, storage, and management functions use the same nodes. The use of hyperconverged architecture allows:
- Effectively use all available resources;
- Unify the equipment used and simplify its configuration;
- Reduce the volume of spare parts;
- Simplify cloud scaling.
Cloud High Availability
High availability is ensured by architectural solutions and infrastructure services built into AccentOS:
- Launching the cloud controller and database in the form of a VM with the ability to restart each of the VMs in the event of an accident. (using Zabbix);
- Cloud controller VM clustering and load balancing between VMs;
- Clustering of VM databases (Galera software ensures auto-recovery and integrity of VMs in case of errors and accidents);
- Launching SDS Ceph to ensure disaster-resilience of the cloud storage system (Ceph software provides balancing, uniform load distribution, and automatic data recovery in case of disasters).
Automatic cloud recovery
Inclusion in the cloud architecture of a module for comprehensive analysis of the operation of cloud components that performs:
- Autostart of a backup node if one of the cloud nodes fails;
- Autostart of client VMs on another cloud node;
- Regular automatic testing of all cloud modules and services;
- Automatic control of network services DNS, NTP, HAProxy and automatic switching to backup routes;
- Automatic recovery of RabbitMQ, Redis, ETCD services if they are detected to be frozen;
- Automatic restart of Neutron, Nova, Cinder, Glance, Celliometer modules if they freeze.
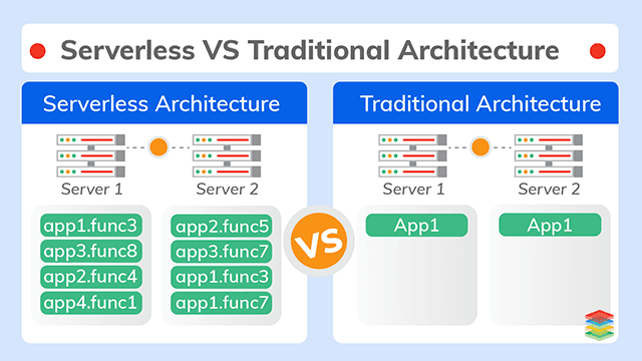
API and Serverless management
AccentOS includes API OpenStack, Ceph, AccentOS modules, allowing you to create serverless applications (Iaa-Code), projects, PaaS, sandboxes. For this, VMs (KVM), containers (LXC, Docker) can be used, which allows:
- Automatically start and stop projects, VMs or containers at the right time, indicating allocated resources and included applications;
- Launch projects from applications (IaaC);
- Use resources at the right time to achieve results;
- Assign the required amount of resources.
Running Kubernetes via API
AccentOS (OpenStack) supports working with pods through the ZUN module.
AccentOS (OpenStack) supports working with Kubernetes-aaS through the MAGNUM module.
Migration of VmWare to AccentOS
- Migration utility to RAW / QCOW2 formats;
- Changing the composition of drivers;
- Changing configuration and network settings;
- Integration with cloud templates;
- Initialization at startup;
- Embedding a self-testing system to check the correctness of the conversion.
Installing VM software using the AppLevel API
AccentOS allows automatic generation of a VM image with a set of applications available in the library. Unlike the traditional method of installing applications inside a VM and then preparing a “golden image”. Performing these actions is possible through the AppLevel WEB interface or through the system API.
This feature allows you to:
- Automatically dynamically include applications available in the library into the “golden image” of the guest VM via the API;
- Install an unlimited number of applications simultaneously in a very short time in API mode or selection via WEB;
- Does not require additional testing of the VM after adding applications;
- Consider the cost of added applications;
- Display in the VM template the composition of applications included in the “golden image”.
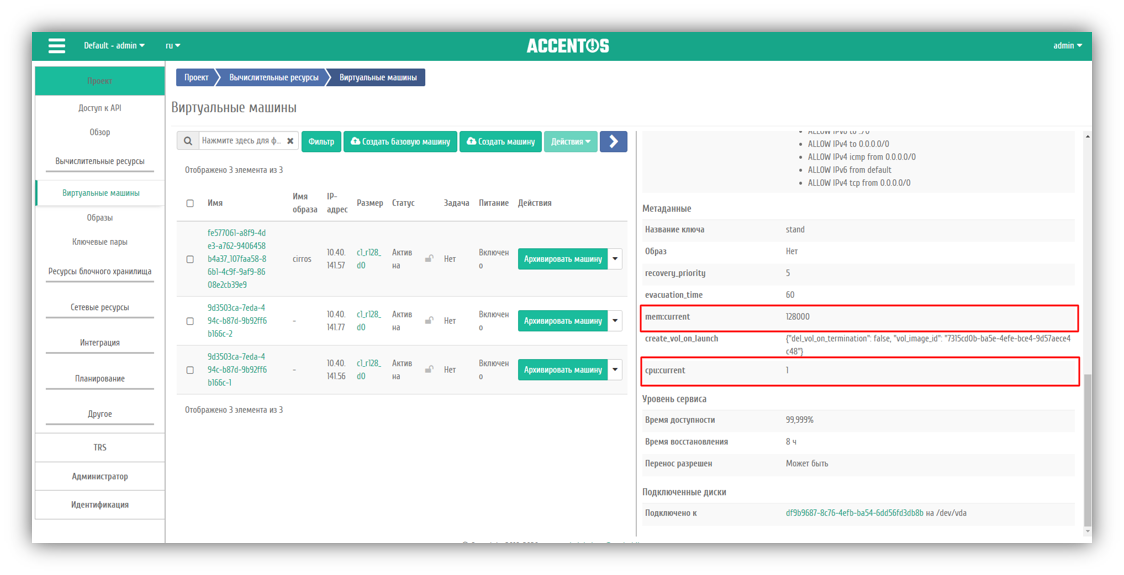
Resizing VMs on the fly
AccentOS provides:
- Change RAM size on the fly;
- Changing disk (volume) size on the fly;
- Changing the number of VM CPU cores on the fly;
- Changing QoS for CPU on the fly.
AccentOS and StorageSpace
AccentOS extends and manages Sanlock functionality for applications running on clusters of shared storage hosts.
Management and coordination are performed through reading and writing blocks on the shared storage system.
Live migration of block devices
AccentOS provides live migration of block devices and file volumes between storage systems:
- With various iSCSI, FC interfaces;
- Between different types of storage systems (SAS, SATA);
- Between different pools;
- Between different storage systems.
AccentOS Autorecovery
Autorecovery module is a system for automatic recovery of the cloud infrastructure, uses information from the monitoring module and from the logging system to inform the administrator about a possible malfunction and auto-recovery of cloud services.
When making a decision, the system uses AI functionality, which at this stage of development identifies single failure errors of cloud services and sends a command via the API to restore them.
As the AI system learns and increases in complexity, it will have:
- functionality for predicting possible faults for the administrator,
- functionality of regularly recurring errors in the functioning of cloud services,
- functionality for identifying and recovering complex errors in the functioning of cloud services.
AccentOS
virtualization of workstations and applications
VDI compliance
- Support Windows Srv, Windows 7/8/10/11, Linux;
- Integration with MS AD/OpenLDAP/FreeIPA/Samba;
- Management via LDAP of profiles and personal folders;
- Support for two-factor authentication system, smart cards;
- Running a desktop in a VM or container;
- Support for terminal servers;
- Application delivery;
- Own terminal protocol (forwarding devices and services);
- Thin client management system.
AccentOS VDI and application delivery
Application delivery allows you to work on a PC and in VDI simultaneously, which is useful for working with many VDI servers, multimedia, and video conferencing.
- Delivery of Windows applications via a terminal server;
- Delivery of Linux applications through the LXC container;
- Support for Windows applications using Linux – LXC - WINE;
- Deployment tools for delivered applications;
- Application ordering portal.
Linux desktop for those who are used to Windows
- Desktop indistinguishable from Windows - windows, explorer, settings, names.
- Support for running MS Office applications using WINE.
- Support existing Windows applications using WINE (to be discussed).
- Support for applications using CIPF Crypto-Pro.
AccentOS
implementation and support
Cloud resource management
- Automatic deployment of the platform and IaaS via AccentOS autosetup;
- Automatic deployment and configuration of PaaS;
- Integrated mandatory services (Backup, logging, monitoring, access);
- API for collecting data for charging;
- Platform for ordering operator services OSS/BSS.
Migration of VmWare to AccentOS
Windows VM image migration utilities (VmWare) - Windows (OpenStack KVM):
- Sysinternals utilities
- Acronis backup
Linux (VmWare) - Linux (OpenStack KVM) migration utilities:
Procedure for converting a VmWare VM:
-
Launching the conversion utility
-
Checking the health of the VM
Procedure for converting a VmWare project:
-
Creating a project in AccentOS similar to VmWare with setting up VM networks
-
Launching the conversion utility for the project VM
-
Checking the functionality of the project in OpenStack
AccentOS support
AccentOS provides the following support options.
-
Long-term support for AccentOS in 5x9 and 7x24 Moscow time;
-
Support for AccentOS Standard and Advanced versions;
-
Level 3 support;
-
Customized level 2 and 3 support;
-
Remote and on-site support;
-
Access to documentation on the developer portal;
-
Appeals through the portal, by mail and telephone;
-
Training of customer specialists in cloud platform and desktop virtualization courses.